GEM-CAR FAQ
Brief Definition of Accounting Terms
ASSETS
It is an asset that has value at a given time. For example, your car, your bank account, your accounts receivable, your accounting software... Standard: The code for this account must begin with 1 and is normally DEBTOR.
LIABILITIES
It's what you owe. For example, a line of credit, debt, etc. Standard: The code for this account must begin with 2 and is normally CREDITOR.
CAPITAL
As for capital, it is what you are worth. For example, profit, share capital, etc. If we sell all our assets and pay all our liabilities, capital is what we have left. So you will find the following equation: ASSETS=LIABILITIES+CAPITAL Standard: The code for this account must start with 3 and is normally CREDITOR.
INCOME
It includes all miscellaneous sales items. Standard: The code for this account must begin with 4 and is normally CREDITOR.
EXPENSES
Expenses do not need to be described; it is the easiest thing to do in a business. Standard: The code for this account must begin with 5 and is normally DEBT. Any account in your chart is either normally credit or normally debit. This is simply an accounting convention. You should not try to find a logical explanation if you are not familiar with this convention.
COST OF GOODS SOLD (COGS)
If the expense account you are creating is an expense directly related to your cost of goods sold, enter "Cost of Goods Sold" as the account type. This way, under revenue, you will see your cost of goods sold and gross profit.
Debit The asset and expense accounts are normally in debit.
CREDIT The liabilities, revenue, and capital accounts are normally in credit.
SHORT TERM
Normally achievable within one year (e.g. bank account).
LONG TERM
Normally achievable in more than one year (e.g. Furniture). Always by convention, put short-term accounts before long-term ones.
See our well-visualized example
BANK ACCOUNT
f your account is a bank account from which you draw cheques.
TAXABLE
Check if the account normally affects QST and GST. A number of accounts are included in your software. It is up to you to rename the code if it does not correspond to your accounting code or to change the name to suit your own situation if the system allows it.
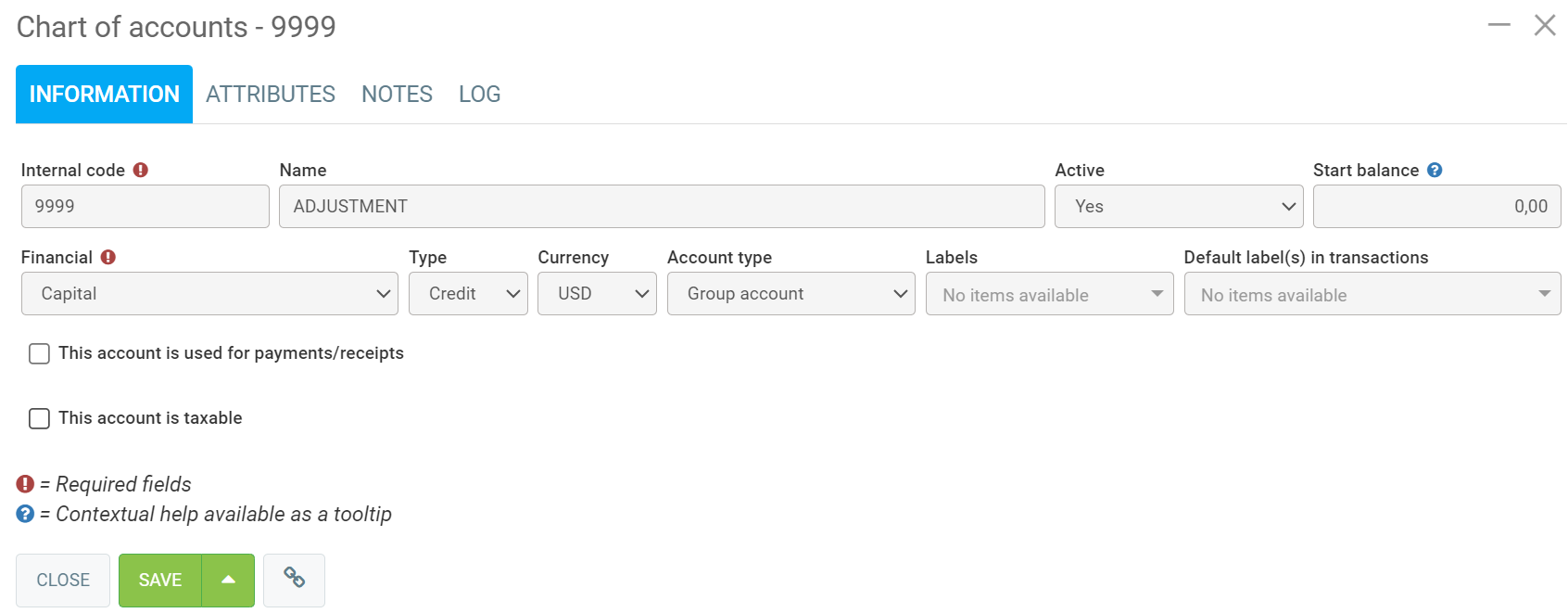
You will notice the last account, code 9999, is transient. It is your choice to have such an account, but we suggest that you have an account whose function is not well-defined. When you are faced with a transaction for which you do not know which account to use, use this account temporarily while you ask your accountant what you should have done.
For "Account Types", here are your choices. As a picture is worth a thousand words, here is an example.
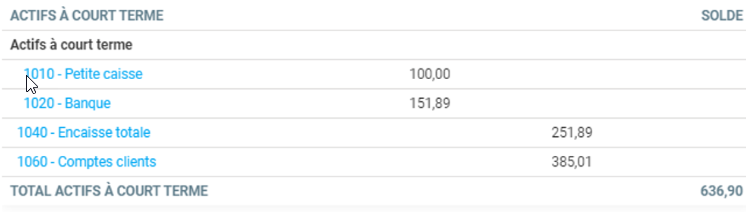
The word 'TAXES' in black is a "Group Header" account type. This type of account cannot be used in a transaction. Accounts 2210 and 2240 are "Group Accounts", which are normal accounts, but since they are preceded by a If you select "Group header", they are printed with a slight indentation. Finally, account 2260 is a "Group Total" account, it displays the group total. This type of account cannot be used in a transaction.
An adjustment account is mainly used as a temporary account during an import. We suggest using the "Adjustments" account that we code with the letters AJ when importing a charter, detailed in the following sections.
PROFIT
A small note for the profit accounts.
- Retained earnings
- Ongoing benefits
- Net income
The one that is configured in GEM-BOOKS is the account that will be used to accumulate the operation profits, in short, the one that will accumulate your profits. We suggest using the "Current Profits" account that we code with the letters BF when importing a charter.
Posted
9 months
ago
by
Olivier Brunel
#430
75 views
Edited
6 months
ago
